Article -> Article Details
| Title | A Practical Guide to Deal with Scabies |
|---|---|
| Category | Fitness Health --> Beauty |
| Meta Keywords | ivermectin, scabies, skin care, online generic medicine, |
| Owner | Ben Taylor |
| Description | |
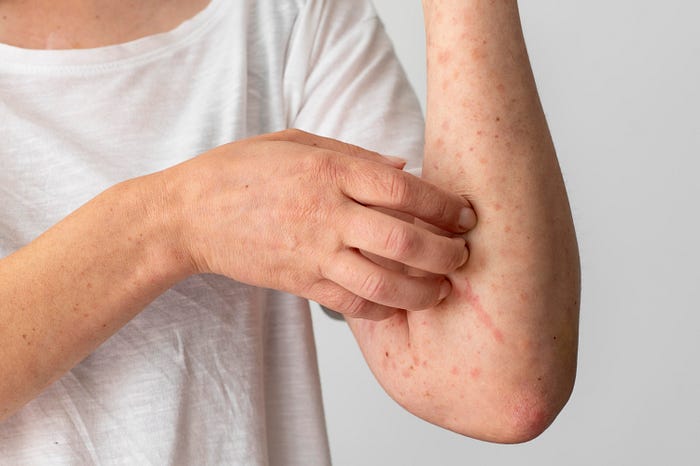 Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. Although the condition might sound alarming, understanding its nature, symptoms, and prevention methods can help mitigate its effects and stop its spread. What Is Scabies?At its core, scabies is an infestation where mites burrow into the outer layer of the skin to lay eggs. This process triggers the body’s immune response, leading to itching, rashes, and other symptoms. Despite its unpleasant nature, scabies is treatable with prompt medical attention. The Lifecycle of the Scabies Mite:Understanding the lifecycle of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite is crucial for effective treatment:
This lifecycle typically spans 10 to 14 days, making timely treatment essential to disrupt the cycle. How Do You Contract Scabies?Scabies spreads primarily through direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact. While casual handshakes or brief hugs are less likely to transmit scabies, intimate interactions and shared living spaces significantly increase the risk. Common ways scabies gets transmitted includes:
Recognizing Scabies Symptoms:The symptoms of scabies may take several weeks to appear after the initial infestation. Key signs include:
Commonly affected areas include the webbing between fingers, wrists, elbows, knees, buttocks, and genital regions. In infants and young children, scabies may also affect the scalp, face, neck, and soles of the feet. Complications of Untreated Scabies:Without timely intervention, scabies can escalate into more severe conditions such as:
Diagnosing Scabies:A medical professional can diagnose scabies by examining the skin for characteristic burrows, rashes, or lesions. In some cases, a skin scraping might be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of mites, eggs, or fecal matter. Treatment Options:Effective treatment for scabies involves eliminating the mites and addressing symptoms: Topical Medications:
Oral Medications:
Preventing Scabies:Preventive measures are crucial to curbing the spread of scabies. Key strategies include:
Dispelling Common Myths:Myth: Scabies only affects unclean individuals. Fact: Scabies can affect anyone regardless of hygiene. Myth: Mites can live long without a human host. Fact: Scabies mites survive only 2–3 days off the human body. When to See a Doctor:If you suspect scabies, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Delaying treatment can lead to complications and increase the risk of spreading the condition. Conclusion:Scabies, though uncomfortable and contagious, is entirely manageable with the right approach. By recognizing the symptoms early, seeking timely treatment, and adopting preventive measures, you can effectively protect yourself and others from this skin condition. For affordable treatments and trusted advice, visit Online Generic Medicine. Safeguard your skin and health today! | |
