Article -> Article Details
| Title | Benefits of Fiber: What Happens If You Eat Too Much Dietary Fiber? |
|---|---|
| Category | Fitness Health --> Health Articles |
| Meta Keywords | Benefits of Fiber |
| Owner | Dr Good Deed |
| Description | |
|
Understanding the Benefits of Fiber in Your DietFiber plays a vital role in keeping your digestive system functioning smoothly. It helps regulate bowel movements, stabilizes blood sugar, and improves heart health. But the benefits of fiber depend on balance. Too little leads to constipation, but too much can overwhelm your digestive tract and cause discomfort, especially if you increase intake too quickly. Types of Dietary Fiber and How They WorkSoluble FiberSoluble fiber absorbs water and forms a gel-like texture. It helps manage blood sugar and lowers cholesterol. Foods include oats, apples, beans, and chia seeds. Insoluble FiberInsoluble fiber adds bulk to your stools and promotes regularity. It’s found in whole grains, nuts, and leafy vegetables. Both types contribute to the benefits of fiber, but excessive amounts can cause digestive overload. What Happens If You Eat Too Much Fiber?Eating more fiber than your digestive system can handle may lead to several symptoms. These issues usually appear when intake jumps suddenly or exceeds 40–50 grams per day. Common Side Effects of Excess Fiber
These problems often occur despite the many benefits of fiber, especially when you consume too much too quickly. Why Excess Fiber Causes Digestive ProblemsFiber requires adequate hydration to move smoothly through your digestive system. When water intake is low, stools become hard and bulky. Sudden spikes in fiber also overwhelm gut bacteria, leading to excess fermentation and bloating. Even when the goal is improving gut health, the benefits of fiber can backfire if not balanced properly. How Much Fiber Should You Eat?Most adults need:
Reaching this range supports the benefits of fiber without causing discomfort. Gradual increases are best, especially if your usual intake is low. How to Avoid Problems When Increasing FiberIncrease Intake SlowlyAdd fiber-rich foods week by week. This allows your gut microbiome to adjust. Drink Plenty of WaterAim for at least 6–8 glasses daily to help fiber move easily through your intestines. Choose Balanced SourcesCombine fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains instead of relying on a single type. Listen to Your BodyIf symptoms appear, reduce intake temporarily and reintroduce fiber gradually. When Too Much Fiber Becomes a Health ConcernChronic overconsumption can lead to persistent digestive distress. If symptoms like severe bloating, constipation, or abdominal pain persist, you should seek medical guidance. Even when focusing on the benefits of fiber, your body needs balance to function properly. When to See a DoctorSeek help if you experience:
These may signal conditions unrelated to fiber intake. Final ThoughtsThe benefits of fiber support overall health, but moderation is essential. Eating too much can cause digestive discomfort, nutrient imbalances, and hydration issues. Gradual increases, proper hydration, and a varied diet can help you enjoy the advantages without side effects. FAQ1. Can you eat too much fiber? 2. How much fiber is considered too much? 3. Does too much fiber cause constipation? 4. What helps relieve symptoms of high fiber intake? 5. Can excess fiber cause nutrient deficiencies? 6. How fast should you increase fiber? 7. Can too much fiber make you bloated? 8. Are fiber supplements safe? 9. Should you stop fiber if you feel pain? 10. What is the healthiest way to get fiber? | |

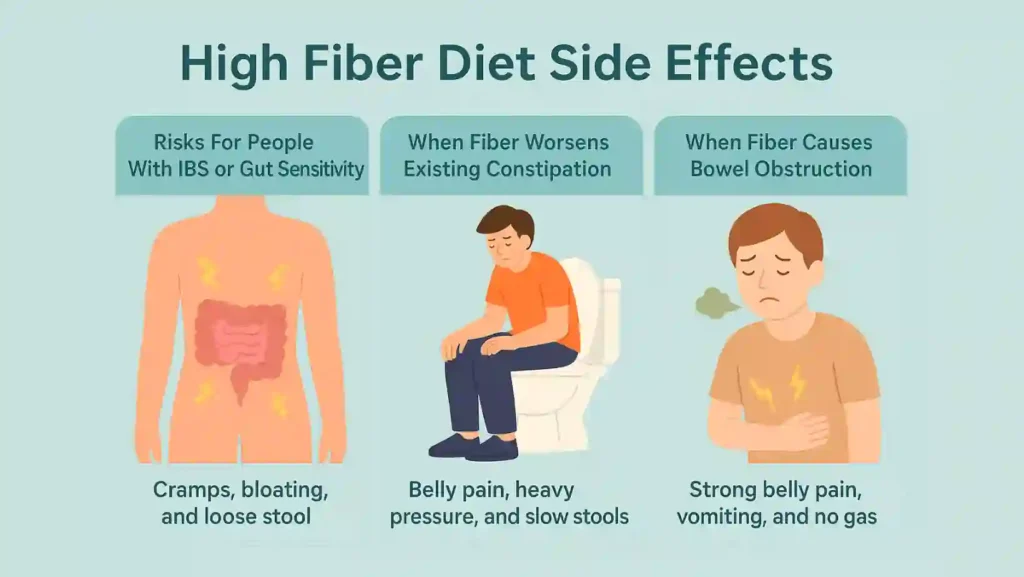 Dietary fiber supports digestion, gut health, and long-term wellness, but eating too much can cause uncomfortable symptoms. While the
Dietary fiber supports digestion, gut health, and long-term wellness, but eating too much can cause uncomfortable symptoms. While the